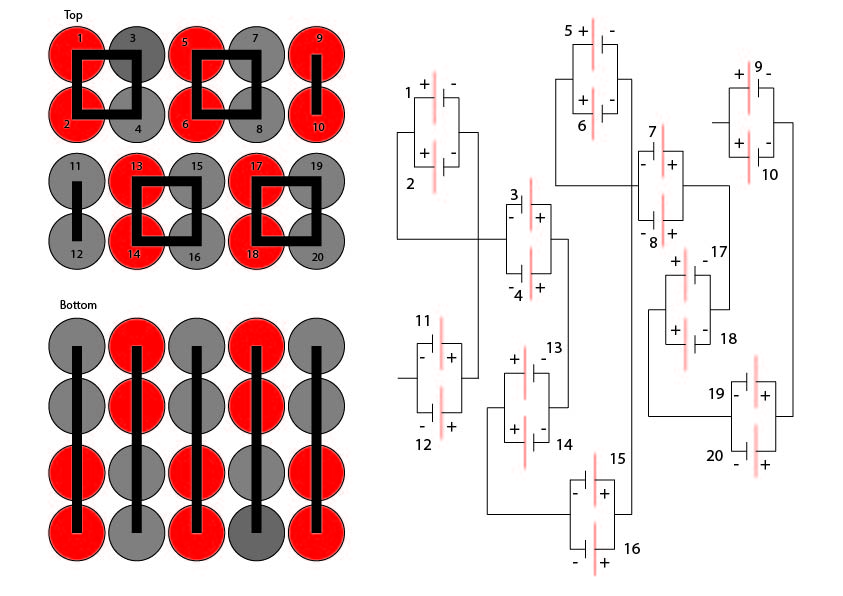
- Details
- Category: Lithium ion Batteries
Definitions
Watt
In electricity, watts (W) is the unit of measurement for power, which indicates the rate at which energy is used or generated. One watt is equivalent to one joule of energy per second.
Watts(W) measures power which is the rate of energy flow.
The electrical formula is Power(W) = Volts(v) x Current (I)
Watt-hours(Wh) or kilowatt-hours(kWh) measures the total amount of energy used over time
-
Power vs. Energy:Watts (W) measure power, which is the rate of energy flow. Watt-hours (Wh) or kilowatt-hours (kWh) measure the total amount of energy used over time.
-
Calculating Watts:Watts are calculated by multiplying voltage (Volts) by current (Amps). For example, a device using 10 amps at 120 volts has a power consumption of 1200 watts (10A * 120V = 1200W).
-
Real-world examples:A 60-watt light bulb consumes 60 joules of energy every second it is on. A 1000-watt microwave oven consumes 1000 joules of energy per second.
-
Kilowatts:Larger power consumption is often measured in kilowatts (kW), where 1 kW equals 1000 watts.
EV Battery Characteristics
- Battery Capacity
- C-Rate
Battery Capacity
Battery capacity or Energy capacity is the ability of a battery to deliver a certain amount of power over a while. It is measured in kilowatt-hours (product of voltage and ampere-hours). It determines the energy available to the motor and other elements. The rate is dependent on the amount of current being transferred by the battery as the voltage is usually constant. So scientifically it is denoted as only Ah.
How battery capacity affects range?
A car’s range depends on its battery’s capacity and efficiency of use. Generally, most vehicles will need 20 to 30kW of power on highways for a steady speed. So, accordingly, a 60-kWh battery may allow up to three hours of travel. Though keep in mind that other factors such as speed or outside temperature influence the battery discharge rate.
Measurement of battery capacity
Battery capacity is measured in two different metrics:
Gross or Total Capacity
It is the total amount of energy theoretically held by the battery.
Net or Usable Capacity
This is the energy that a car can actually draw on to propel itself.
The difference is created by automakers to prevent the full charge and discharge of the battery. This damages or shortens the battery’s life.
Battery capacities of some common EVs
- Tesla ModelS/Model X:100kWh battery.
- Mercedes Benz EQS:115 kWh or maybe more.
- Rivian R1T:135kWh battery.
A C-rating is used to define the rate at which a battery is fully charged or discharged. For instance, when the vehicle with an 85kWh battery is charged at a C-rate of 1C means that it is charged to its full capacity i.e. 85kW in one hour.
For more than 1C means a faster charge. So, at a 3C rate, the time will be 1/3 times. It means that full capacity can be charged in 20 minutes and simultaneously the power delivered thrice means 255kW. Similarly, lower C-rate means a slower charge, at C/5 means the battery will be charged to its full capacity in 5 hours with 17kW.
How C-Rate affect battery life?
In ideal conditions, the battery might perform at extremely high C-rates. But practically as the C-rate increases, it is difficult for the battery to deliver reliable performance. A higher C-rate increases the degradation rate of a battery, resulting in a reduced range, safety, and lifespan.
This happens due to increased temperature and mass transfer limitations. This is the main obstacle to the wide adoption of EVs, increasing the charging time.
- Details
- Category: Lithium ion Batteries
- Details
- Category: Lithium ion Batteries
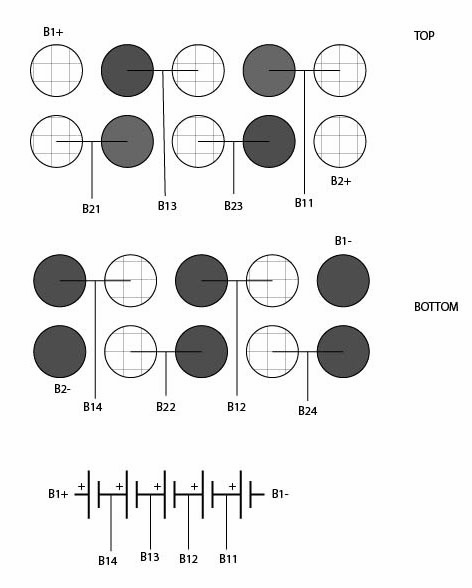 Product Information
Product Information
-
Battery Type:
Samsung Lithium Ion
Xell 3.7v R18650-2500 x 10 -
Dimensions:
12.2 x 7.9 x 6.9cm (approx.)
weight 668g -
Rechargeable:
95 minute charging time (approx.)
-
Voltage:
20-40V
20V 5.0Ah
40v 2.5Ah - Power 90Wh

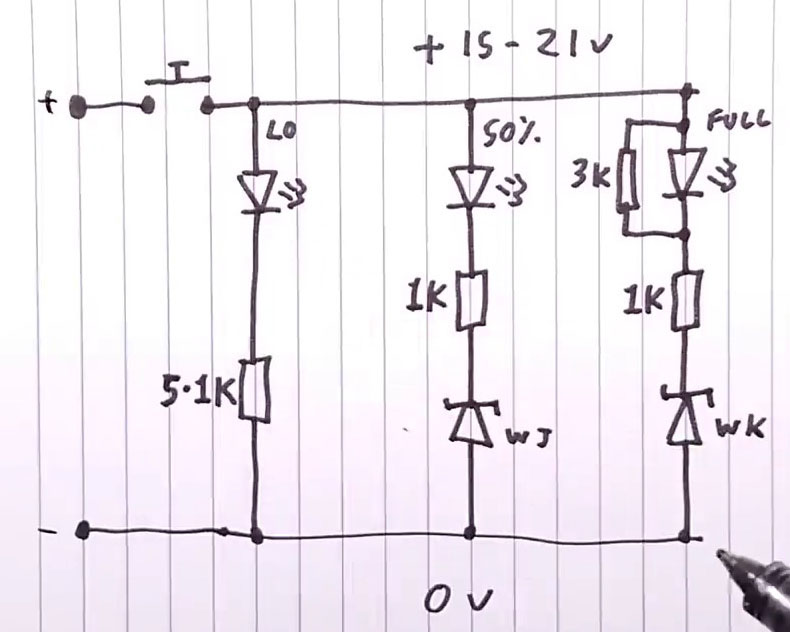

yendifplayer mp4=/images/videos/ebikes/Inside_An_Aldi_20_40V_Battery.mp4
- Details
- Category: Lithium ion Batteries
| Long-Form Name | Chemical Abbreviation | Name Format 1 | Name Format 2 | Name Format 3 |
| Lithium Manganese Oxide | LiMn2O4 | IMR | LMO | Li-Manganese |
| Lithium Manganese Nickel | LiNiMnCoO2 | INR | NMC | --- |
| Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide | LiNiCoAlO2 | --- | NCA | Li-Aluminum |
| Lithium Nickel Cobalt Oxide | LiNiCoO2 | --- | NCO | --- |
| Lithium Cobalt Oxide | LiCoO2 | ICR | LCO | Li-Cobalt |
| Lithium Iron Phosphate | LiFePO4 | IFR | LFP | Li-Phosphate |