- Details
- Category: ESP32
Based on the Espressif ESP32-S3-WROOM-1 microcontroller
and
Sitronix ST7262 800RGB x 480 dual gate TFT-LCD panel
Arduino IDE Setup Notes
Board Configuration
Initial testing
1st make use this BareMinimum sketch to make sure you can upload to the board.
- If the sketch does not upload try changing the Upload speed to 11520
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
}
void loop() {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
}Install ESP32_Display_Panel library with library manager
ESP32_Display_Panel is a library designed for ESP SoCs to drive display panels and facilitate rapid GUI development.
You might get the following message:
The library ESP32_Display_Panel: 1.0.0 needs some other library dependencies currently not installed
ESP32_IO_Expander
esp-lib-utils
Would you like to install also all the missing dependencies?
Click 'yes' to install ESP32_IO_Expander
ESP32_IO_Expander must be version 0.1.0 so after installation go into 'Manage Libraries and downgrade it.
Open Examples->ESP32_Display_Panel->arduino->board_static_config
save the exaple as a new name such as myboard_static_config
Follow the steps below to configure:
1 In the Arduino IDE choose an ESP board and configure its parameters. Make sure PSRAM is enabled
Waveshare ESP32-S3-Touch-LCD-7

Can work using ESP32S3 Dev Module

2 Follow the setup for supported boards. here
- Set the
ESP_PANEL_USE_SUPPORTED_BOARDmacro definition in theESP_Panel_Board_Supported.hfile to1. - Uncomment the corresponding macro definition for the target development board model.
- If the sketch does not upload try changing the Upload speed to 115200
For the Arduino IDE you have to move examples and demos down to the src folder because the Arduino IDE only references the library's source folder
- Details
- Category: ESP32
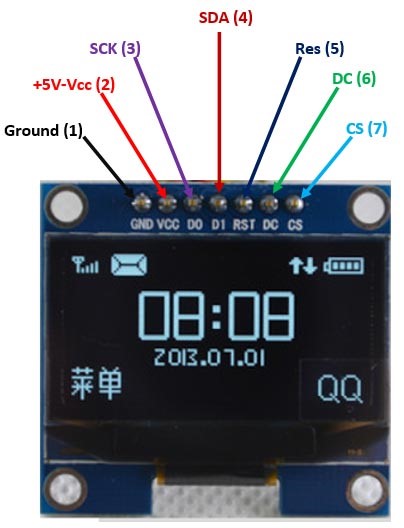

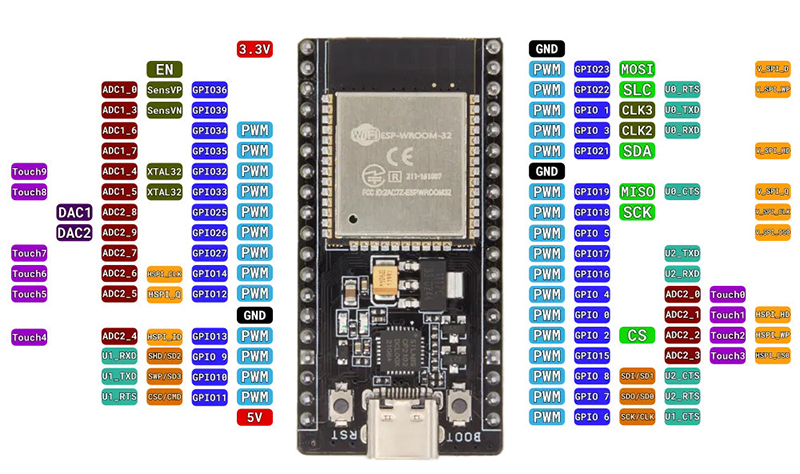
Pins
| Pin | Colour | Other | Desc | ESP32 | UNO | ||
| 1 | GND | Black | |||||
| 2 | VCC | Red | |||||
| 3 | D0 | Brown | SCK | SCLK (SD-Clock) | SPI Clock | 14 | 13 |
| 4 | DI | White | SDA | MOSI | SPI Master out Slave in | 13 | 11 |
| 5 | RES | Purple | RES | MISO | SPI Master in Slave out Reset | 17 | 12 |
| 6 | DC | Grey | DC | 16 | |||
| 7 | CS | Yellow | CS | Chipselect | 15 | 10 |